因为是初学RocketMQ,为了更快速上手,所以直接从rocketmq-spring-boot-samples 示例开始。
⚠️注意:rocketmq-spring-boot-starterRocketMQ 4.x 客户端 ,主要面向依赖于 RocketMQ 4.x 的应用。
rocketmq-produce-demo
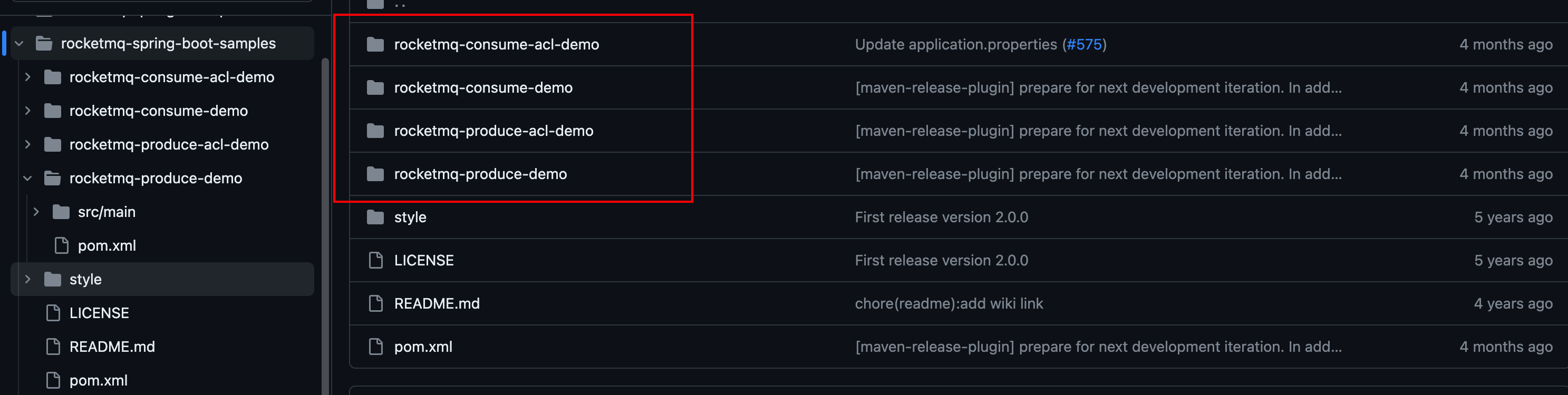
进入到 rocketmq-spring-boot-samples 项目中,会发现如下模块:
从名称可以看出,客户端-生产者分为普通demo和acl-demo两种,消费者也是如此。
在RocketMQ中,ACL的含义是访问控制表(Access Control List,ACL)描述用户或角色对资源的访问控制权限。简单点说,ACL就是控制指定用户是否对指定主题和消费组是否具有发送和消费的权限。
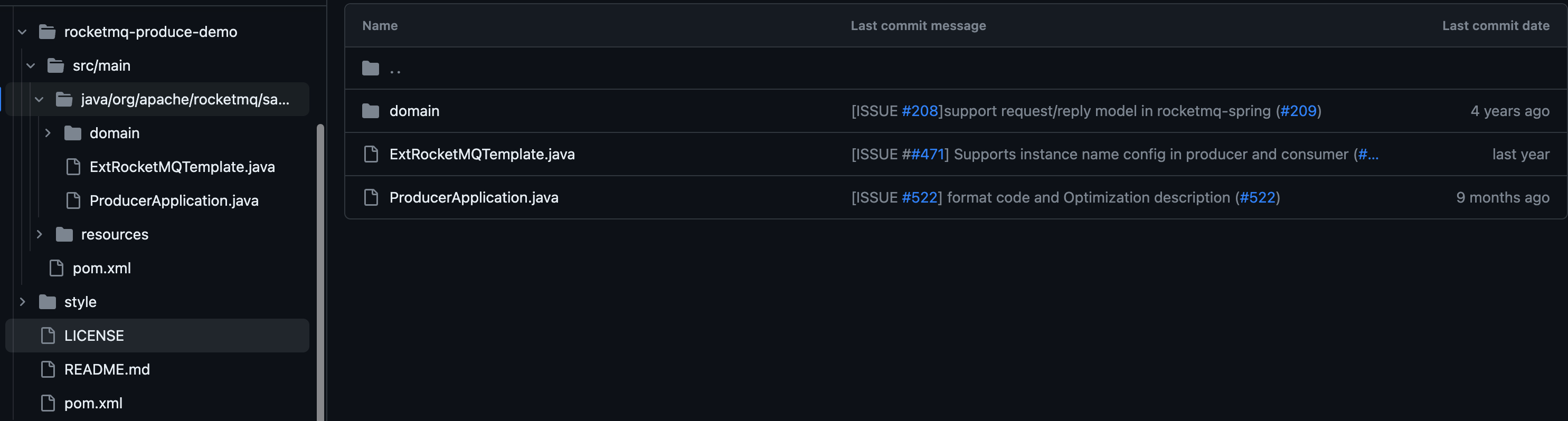
既然是初学,就从普通demo开始,等后面高级进阶再展开了解acl-demo。rocketmq-produce-demo的项目结构如下:
ProducerApplication是一个SpringBootApplication,它注入了RocketMQTemplate和一些Topic名称,通过rocketMQTemplate向指定topic发送消息,简略代码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 @SpringBootApplication public class ProducerApplication implements CommandLineRunner { @Resource private RocketMQTemplate rocketMQTemplate; @Value("${demo.rocketmq.topic}") private String springTopic; public static void main (String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(ProducerApplication.class, args); } @Override public void run (String... args) throws Exception { SendResult sendResult = rocketMQTemplate.syncSend(springTopic, "Hello, World!" ); System.out.printf("syncSend1 to topic %s sendResult=%s %n" , springTopic, sendResult); } }
通过run方法可以看到rocketMQTemplate.syncSend就是生产者发送消息的实现方法,关键对象就是RocketMQTemplate,它是通过spring依赖注入进来的,那么现在就观察它是如何注册到spring容器中的。
因为RocketMQTemplate没有显式构造方法,因此直接在class类上打断点,启动Application,可以发现其在RocketMQAutoConfiguration#rocketMQTemplate方法下被实例化。熟悉SpringBoot自动装配的话,可以猜到在rocketmq-spring-boot模块下会有spring.factories,找到EnableAutoConfiguration的实现类也是RocketMQAutoConfiguration,其源码大致如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 @Configuration @EnableConfigurationProperties(RocketMQProperties.class) @ConditionalOnClass({MQAdmin.class}) @ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "rocketmq", value = "name-server", matchIfMissing = true) @Import({MessageConverterConfiguration.class, ListenerContainerConfiguration.class, ExtProducerResetConfiguration.class, ExtConsumerResetConfiguration.class, RocketMQTransactionConfiguration.class, RocketMQListenerConfiguration.class}) @AutoConfigureAfter({MessageConverterConfiguration.class}) @AutoConfigureBefore({RocketMQTransactionConfiguration.class}) public class RocketMQAutoConfiguration implements ApplicationContextAware { public static final String ROCKETMQ_TEMPLATE_DEFAULT_GLOBAL_NAME = "rocketMQTemplate" ; public static final String PRODUCER_BEAN_NAME = "defaultMQProducer" ; public static final String CONSUMER_BEAN_NAME = "defaultLitePullConsumer" ; @Autowired private Environment environment; private ApplicationContext applicationContext; @PostConstruct public void checkProperties () { String nameServer = environment.getProperty("rocketmq.name-server" , String.class); log.debug("rocketmq.nameServer = {}" , nameServer); if (nameServer == null ) { log.warn("The necessary spring property 'rocketmq.name-server' is not defined, all rockertmq beans creation are skipped!" ); } } @Bean(PRODUCER_BEAN_NAME) @ConditionalOnMissingBean(DefaultMQProducer.class) @ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "rocketmq", value = {"name-server", "producer.group"}) public DefaultMQProducer defaultMQProducer (RocketMQProperties rocketMQProperties) { } @Bean(CONSUMER_BEAN_NAME) @ConditionalOnMissingBean(DefaultLitePullConsumer.class) @ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "rocketmq", value = {"name-server", "pull-consumer.group", "pull-consumer.topic"}) public DefaultLitePullConsumer defaultLitePullConsumer (RocketMQProperties rocketMQProperties) throws MQClientException { } @Bean(destroyMethod = "destroy") @Conditional(ProducerOrConsumerPropertyCondition.class) @ConditionalOnMissingBean(name = ROCKETMQ_TEMPLATE_DEFAULT_GLOBAL_NAME) public RocketMQTemplate rocketMQTemplate (RocketMQMessageConverter rocketMQMessageConverter) { } static class ProducerOrConsumerPropertyCondition extends AnyNestedCondition { public ProducerOrConsumerPropertyCondition () { super (ConfigurationPhase.REGISTER_BEAN); } @ConditionalOnBean(DefaultMQProducer.class) static class DefaultMQProducerExistsCondition { } @ConditionalOnBean(DefaultLitePullConsumer.class) static class DefaultLitePullConsumerExistsCondition { } } }
RocketMQAutoConfiguration注册了三个Bean(DefaultMQProducer、DefaultLitePullConsumer、RocketMQTemplate),看一下RocketMQTemplate的注册条件:
spring容器中需要存在DefaultMQProducer和DefaultLitePullConsumer两个Bean。
容器中没有注册过bean名称为rocketMQTemplate的Bean。
再看RocketMQTemplate注册为Bean的实现方法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 public RocketMQTemplate rocketMQTemplate (RocketMQMessageConverter rocketMQMessageConverter) { RocketMQTemplate rocketMQTemplate = new RocketMQTemplate (); if (applicationContext.containsBean(PRODUCER_BEAN_NAME)) { rocketMQTemplate.setProducer((DefaultMQProducer) applicationContext.getBean(PRODUCER_BEAN_NAME)); } if (applicationContext.containsBean(CONSUMER_BEAN_NAME)) { rocketMQTemplate.setConsumer((DefaultLitePullConsumer) applicationContext.getBean(CONSUMER_BEAN_NAME)); } rocketMQTemplate.setMessageConverter(rocketMQMessageConverter.getMessageConverter()); return rocketMQTemplate; }
可以发现,RocketMQTemplate将生产者、消费者、消息类型转换器都集中在一起,做了一个统一模板。因此RocketMQTemplate除了发送消息外,还可以拉取消息并转换成客户端想要的消息类型。
生产者发送消息原理
跟踪进入rocketMQTemplate.syncSend方法中。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 public SendResult syncSend (String destination, Message<?> message, long timeout, int delayLevel) { if (Objects.isNull(message) || Objects.isNull(message.getPayload())) { log.error("syncSend failed. destination:{}, message is null " , destination); throw new IllegalArgumentException ("`message` and `message.payload` cannot be null" ); } try { org.apache.rocketmq.common.message.Message rocketMsg = this .createRocketMqMessage(destination, message); if (delayLevel > 0 ) { rocketMsg.setDelayTimeLevel(delayLevel); } SendResult sendResult = producer.send(rocketMsg, timeout); return sendResult; } catch (Exception e) { log.error("syncSend failed. destination:{}, message:{}, detail exception info: " , destination, message, e); throw new MessagingException (e.getMessage(), e); } }
这里面producer.send方法的producer就是RocketMQ的生产者对象了,对象类型为DefaultMQProducer,再进入方法内部看看发送消息的原理。
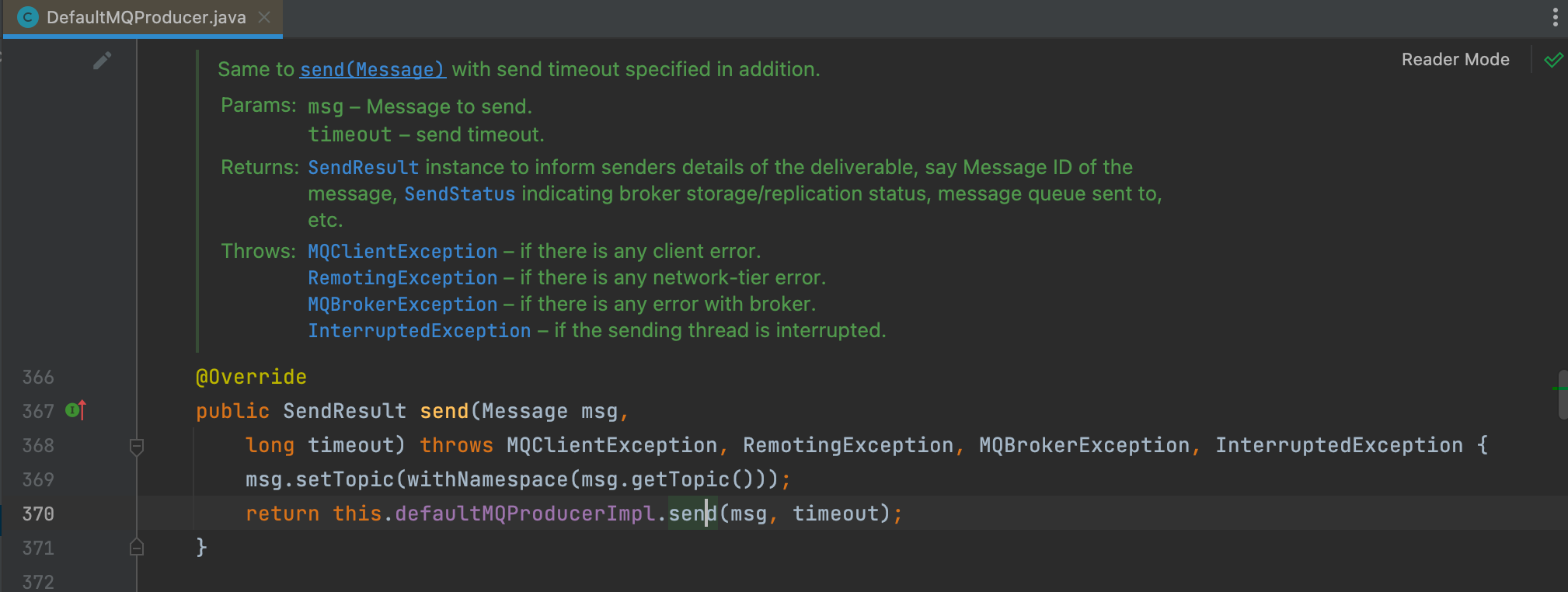
可以发现DefaultMQProducer更像是一个代理类,具体实现类为DefaultMQProducerImpl,进入实现类的DefaultMQProducerImpl#send方法。
1 2 3 4 public SendResult send (Message msg, long timeout) throws MQClientException, RemotingException, MQBrokerException, InterruptedException { return this .sendDefaultImpl(msg, CommunicationMode.SYNC, null , timeout); }
send方法又调用内部的DefaultMQProducerImpl#sendDefaultImpl实现方法。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 private SendResult sendDefaultImpl ( Message msg, final CommunicationMode communicationMode, final SendCallback sendCallback, final long timeout ) throws MQClientException, RemotingException, MQBrokerException, InterruptedException { this .makeSureStateOK(); Validators.checkMessage(msg, this .defaultMQProducer); final long invokeID = random.nextLong(); long beginTimestampFirst = System.currentTimeMillis(); long beginTimestampPrev = beginTimestampFirst; long endTimestamp = beginTimestampFirst; TopicPublishInfo topicPublishInfo = this .tryToFindTopicPublishInfo(msg.getTopic()); if (topicPublishInfo != null && topicPublishInfo.ok()) { boolean callTimeout = false ; MessageQueue mq = null ; Exception exception = null ; SendResult sendResult = null ; int timesTotal = communicationMode == CommunicationMode.SYNC ? 1 + this .defaultMQProducer.getRetryTimesWhenSendFailed() : 1 ; int times = 0 ; String[] brokersSent = new String [timesTotal]; for (; times < timesTotal; times++) { String lastBrokerName = null == mq ? null : mq.getBrokerName(); MessageQueue mqSelected = this .selectOneMessageQueue(topicPublishInfo, lastBrokerName); if (mqSelected != null ) { mq = mqSelected; brokersSent[times] = mq.getBrokerName(); try { beginTimestampPrev = System.currentTimeMillis(); if (times > 0 ) { msg.setTopic(this .defaultMQProducer.withNamespace(msg.getTopic())); } long costTime = beginTimestampPrev - beginTimestampFirst; if (timeout < costTime) { callTimeout = true ; break ; } sendResult = this .sendKernelImpl(msg, mq, communicationMode, sendCallback, topicPublishInfo, timeout - costTime); endTimestamp = System.currentTimeMillis(); this .updateFaultItem(mq.getBrokerName(), endTimestamp - beginTimestampPrev, false ); switch (communicationMode) { case ASYNC: return null ; case ONEWAY: return null ; case SYNC: if (sendResult.getSendStatus() != SendStatus.SEND_OK) { if (this .defaultMQProducer.isRetryAnotherBrokerWhenNotStoreOK()) { continue ; } } return sendResult; default : break ; } } catch (RemotingException | MQClientException | MQBrokerException | InterruptedException e) { endTimestamp = System.currentTimeMillis(); this .updateFaultItem(mq.getBrokerName(), endTimestamp - beginTimestampPrev, true ); log.warn(String.format("sendKernelImpl exception, resend at once, InvokeID: %s, RT: %sms, Broker: %s" , invokeID, endTimestamp - beginTimestampPrev, mq), e); log.warn(msg.toString()); exception = e; } } else { break ; } } if (sendResult != null ) { return sendResult; } throw exception; } validateNameServerSetting(); throw new MQClientException ("No route info of this topic: " + msg.getTopic() + FAQUrl.suggestTodo(FAQUrl.NO_TOPIC_ROUTE_INFO), null ).setResponseCode(ClientErrorCode.NOT_FOUND_TOPIC_EXCEPTION); }
从DefaultMQProducerImpl#sendDefaultImpl方法这个代码量也可以看出,这里就是RocketMQ生产者发送消息的关键代码了,方法的每一行步骤都进行了注释说明,现在对其做个总结:
校验服务器、校验参数,初始化一些记录值,例如时间戳。
根据topic名称获取TopicPublishInfo。
根据TopicPublishInfo获取准备发送的消息队列(MessageQueue)。
调用内核的发送消息实现方法(sendKernelImpl),参数大致有消息body、消息队列MessageQueue、发送方式CommunicationMode、异步发送时的回调方法SendCallback、topic信息TopicPublishInfo、超时时间timeout。
记录发送消息后broker的状态,通过耗时判断broker是否正常运行。
如果发送方式是同步发送,在发送失败后,判断是否需要重试发送。
通过总结,可以发现DefaultMQProducerImpl#sendDefaultImpl其实更多的是在做发送消息前的准备工作,以及发送失败后的重试工作和异常处理工作。所以需要继续往下看,DefaultMQProducerImpl#sendKernelImpl方法的实现原理。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 private MQClientInstance mQClientFactory;switch (communicationMode) { case SYNC: long costTimeSync = System.currentTimeMillis() - beginStartTime; if (timeout < costTimeSync) { throw new RemotingTooMuchRequestException ("sendKernelImpl call timeout" ); } sendResult = this .mQClientFactory.getMQClientAPIImpl().sendMessage( brokerAddr, brokerName, msg, requestHeader, timeout - costTimeSync, communicationMode, context, this ); break ; }
MQClientAPIImpl#sendMessage在发送同步消息时,又会调用内部的sendMessageSync方法。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 private final RemotingClient remotingClient;private SendResult sendMessageSync ( final String addr, final String brokerName, final Message msg, final long timeoutMillis, final RemotingCommand request ) throws RemotingException, MQBrokerException, InterruptedException { RemotingCommand response = this .remotingClient.invokeSync(addr, request, timeoutMillis); assert response != null ; return this .processSendResponse(brokerName, msg, response, addr); }
RemotingClient的实现类则是NettyRemotingClient,由此可知RocketMQ使用Netty作为底层网络编程框架。
在MQClientAPIImpl中纵观其他方法,可以推断RocketMQ的Client与Server交互都是基于此类,例如创建topic、发送消息、拉取消息、心跳检测等。
小结 :
生产者的核心类大致为 DefaultMQProducer -> DefaultMQProducerImpl -> MQClientInstance -> MQClientAPIImpl -> RemotingClient 。
DefaultMQProducer:生产者的包装类,提供多样的消息发送方式,以及控制消息发送时的行为。
DefaultMQProducerImpl:生产者的实现类,用于生产者对象与客户端Client的交互,为生产者提供服务,将生产者注册到服务端Server。
MQClientInstance:RocketMQ客户端的实例,用于客户端Client与服务端Server的交互,为客户端的生产者和消费者提供接口服务。
MQClientAPIImpl:RocketMQ客户端API层的实现类,为客户端提供服务端的API,并管理远程通信对象(RemotingClient)。
RemotingClient:RocketMQ底层实现网络通信的客户端工具,默认实现类为NettyRemotingClient。
生产者核心参数
在使用过程中,用户一般只与DefaultMQProducer进行交互,所以着重关注它下面的变量参数。
InternalLogger log = ClientLogger.getLog()
客户端的日志实现类,RocketMQ 客户端的日志路径为 ${user.home}/logs/rocketmqlogs/rocketmq_client.log。在排查问题时可以从日志文件下手,寻找错误日志,为解决问题提供必要的信息。其中 user.home 为用户的主目录。
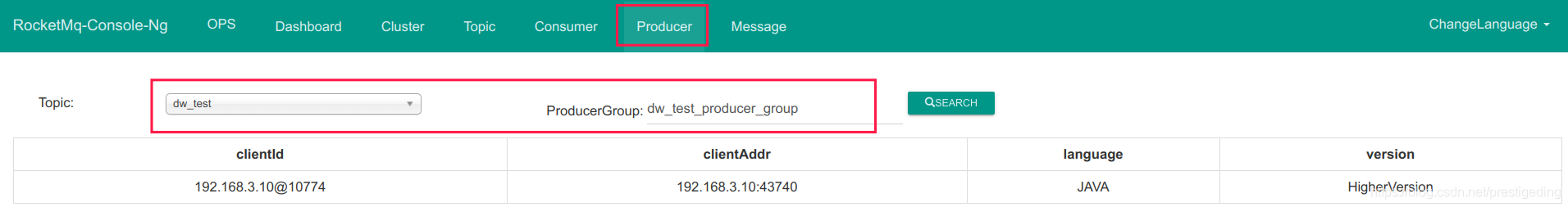
String producerGroup
发送者所属组,开源版本的 RocketMQ,发送者所属组主要的用途是事务消息,Broker 需要向消息发送者回查事务状态。可以通过相关命令或 RocketMQ-Console 查看某一个 Topic 指定消费组的客户端,如下图所示:
int defaultTopicQueueNums = 4
通过生产者创建 Topic 时默认的队列数量。
int sendMsgTimeout = 3000
消息发送默认超时时间,单位为毫秒。值得注意的是在 RocketMQ 4.3.0 版本之前,由于存在重试机制,设置的设计为单次重试的超时时间,即如果设置重试次数为 3 次,则 DefaultMQProducer#send 方法可能会超过 9s 才返回;该问题在 RocketMQ 4.3.0 版本进行了优化,设置的超时时间为总的超时时间,即如果超时时间设置 3s,重试次数设置为 10 次,可能不会重试 10 次,例如在重试到第 5 次的时候,已经超过 3s 了,试图尝试第 6 次重试时会退出,抛出超时异常,停止重试。
int compressMsgBodyOverHowmuch = 1024 * 4
压缩的阔值,默认为 4k,即当消息的消息体超过 4k,则会使用 zip 对消息体进行压缩,会增加 Broker 端的 CPU 消耗,但能提高网络方面的开销。
int retryTimesWhenSendFailed = 2
同步消息发送重试次数。RocketMQ 客户端内部在消息发送失败时默认会重试 2 次。请主要该参数与 sendMsgTimeout 会联合起来生效,详情请参照上文所述。
int retryTimesWhenSendAsyncFailed = 2
异步消息发送重试次数,默认为 2,即重试 2 次,加上第一次发送的次数,所以总共有三次机会。
boolean retryAnotherBrokerWhenNotStoreOK = false
该参数的本意是如果客户端收到的结果不是 SEND_OK,应该是不问源由的继续向另外一个 Broker 重试,但默认设置为false后,就不会触发重试机制。
int maxMessageSize = 1024 * 1024 * 4
允许发送的最大消息体,默认为 4M,服务端(Broker)也有 maxMessageSize 这个参数的设置,故客户端的设置不能超过服务端的配置,最佳实践为客户端的配置小于服务端的配置。
在消息发送失败后,会有重试机制,所以RocketMQ有一个对应的失败策略类MQFaultStrategy,核心参数如下:
boolean sendLatencyFaultEnable = false
是否开启失败延迟规避机制。RocketMQ 客户端内部在重试时会规避上一次发送失败的 Broker,如果开启延迟失败规避,则在未来的某一段时间内不向该 Broker 发送消息,具体机制在本篇的第三部分详细展开。默认为 false,不开启。
long[] latencyMax = {50L, 100L, 550L, 1000L, 2000L, 3000L, 15000L}
设置消息发送的最大延迟级别,默认值为 {50L, 100L, 550L, 1000L, 2000L, 3000L, 15000L},个数与 notAvailableDuration 对应。
long[] notAvailableDuration = {0L, 0L, 30000L, 60000L, 120000L, 180000L, 600000L}
不可用的延迟数组,默认值为 {0L, 0L, 30000L, 60000L, 120000L, 180000L, 600000L},即每次触发 Broker 的延迟时间是一个阶梯的,会根据每次消息发送的延迟时间来选择在未来多久内不向该 Broker 发送消息。
这三个参数,MQFaultStrategy类都提供了setter方法可供修改,在DefaultMQProducer都提供了对应方法。
DefaultMQProducer还继承了ClientConfig类,核心参数如下:
String namesrvAddr = NameServerAddressUtils.getNameServerAddresses()
NameServer 的地址列表。
String clientIP = RemotingUtil.getLocalAddress()
客户端 IP,通过 RemotingUtil#getLocalAddress 方法获取,在 4.7.0 版本中优先会返回不是 127.0.0.1 和 192.168 开头的最后一个 IPV4 或第一个 IPV6。客户端 IP 主要是用来定位消费者的,clientIP 会当成客户端 id 的组成部分。
String instanceName = System.getProperty("rocketmq.client.name", "DEFAULT")
客户端实例名称,是客户端标识 CID 的组成部分。
String unitName
定义一个单元,主要用途:客户端 CID 的组成部分;如果获取 NameServer 的地址是通过 URL 进行动态更新的话,会将该值附加到当中,即可以区分不同的获取 NameServer 地址的服务。
int clientCallbackExecutorThreads = Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors()
客户端 public 回调的线程池线程数量,默认为 CPU 核数,不建议改变该值。
String namespace
客户端命名空间,从 4.5.1 版本被引入。
int pollNameServerInterval = 1000 * 30
客户端从 NameServer 更新 Topic 的间隔,默认值 30s,就 Producer、Consumer 会每隔 30s 向 NameServer 更新 Topic 的路由信息,该值不建议修改。
int heartbeatBrokerInterval = 1000 * 30
客户端向 Broker 发送心跳包的时间间隔,默认为 30s,该值不建议修改。
int persistConsumerOffsetInterval = 1000 * 5
客户端持久化消息消费进度的间隔,默认为 5s,该值不建议修改。
封装生产者工具
RocketMQ生产者对象MQProducer其实已经封装的差不多了,大致就是通过MQProducer对象发送一个Message对象即可,为了让业务层更加方便的使用,不用去了解RocketMQ的Message对象含义,对其进行二次封装。
二次封装的主要作用:
规避RocketMQ的类对象使用。
同一处理消息发送过程,例如日志链路。
同一处理消息发送异常,让业务层感知为运行时异常。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 @Component public class ProducerHelper { private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(ProducerHelper.class); private static MQProducer mqProducer; private static String defaultTopic; public ProducerHelper (@Autowired MQProducer mqProducer, @Value("${rocketmq.demo.topic}") String topic) { ProducerHelper.mqProducer = mqProducer; ProducerHelper.defaultTopic = topic; } public static String send (Object message) { Message msg = buildMessage(message, null , null , null ); return doSend(msg); } public static String send (Object message, String topic) { Message msg = buildMessage(message, topic, null , null ); return doSend(msg); } public static String send (Object message, String topic, String tags) { Message msg = buildMessage(message, topic, tags, null ); return doSend(msg); } public static String send (Object message, String topic, String tags, String keys) { Message msg = buildMessage(message, topic, tags, keys); return doSend(msg); } public static Message buildMessage (Object message, String topic, String tags, String keys) { topic = StringUtils.hasText(topic) ? topic : defaultTopic; byte [] body = JSON.toJSONBytes(message); return new Message (topic, tags, keys, body); } public static String doSend (Message msg) { try { SendResult result = mqProducer.send(msg); log.info("MQ消息发送成功,消息结果: " + result); return result.getMsgId(); } catch (MQClientException | RemotingException | MQBrokerException | InterruptedException e) { log.error("MQ消息发送异常, 消息内容: " + msg, e); throw new RuntimeException (e); } } }